Keeping your muscles healthy will help you be able to walk, run, jump, lift, play sports, and do all the other things you love. Boys and girls have similar amounts of muscle until about age 10, after which puberty increases testosterone levels in males and leads to much greater expansion of skeletal muscle.
Muscle mass declines approximately 3-8% per decade after age 30, and this rate of decline is even higher after age 60.
3 types of muscles and their work
- Skeletal muscles they are connected to your bones by tough cords of tissue called tendons. As the muscle contracts, it pulls on the tendon, which moves the bone. Bones are connected to other bones by ligaments, which are like tendons and help hold your skeleton together.
- Smooth muscles they are also called involuntary muscles since you have no control over them. Smooth muscles work in your digestive system to move food and remove waste from your body.
- Cardiac muscle. Your heart is a specialized type of involuntary muscle. It pumps blood through your body, changing its speed to keep up with the demands you put on it. It pumps more slowly when you sit or lie down and faster when you run or play sports, and your skeletal muscles need more blood to help them do their job.
Top 10 for strengthening your skeletal muscles
Do 60 minutes of exercise every day.
Regular exercise is a great way to build muscle. Try activities that target many different muscles, such as swimming, cycling or dancing. Even simple activities like climbing stairs, jogging and walking are great forms of exercise. Aim for 60 minutes of exercise each day—it’s okay to break your workout into smaller chunks.
Work your biceps.
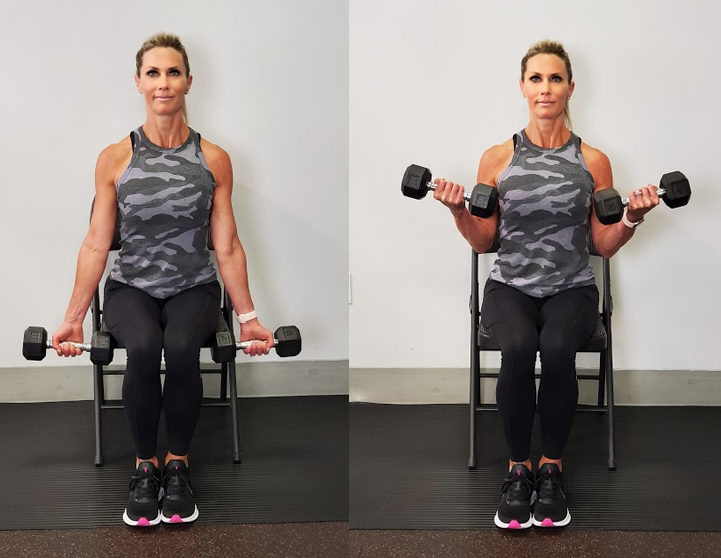
Your biceps are an important skeletal muscle. Dumbbell curls and hammer curls are great options for strengthening your biceps if you have weights at home. Resistance bands are another great way to strengthen your biceps. If you don’t have your own weights, you can make your own set at home.
Target your pecs.
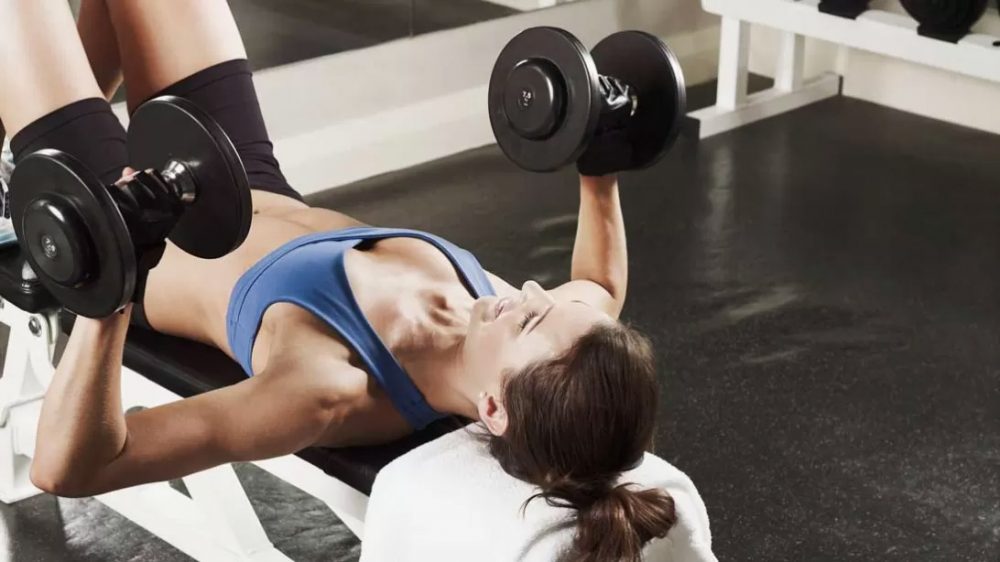

Your pectoral muscles, or front chest muscles, are a valuable skeletal muscle. Bench presses are a great way to strengthen your abs. If you don’t have weights, push-ups are another great way to build that skeletal muscle.
Focus on your quads.
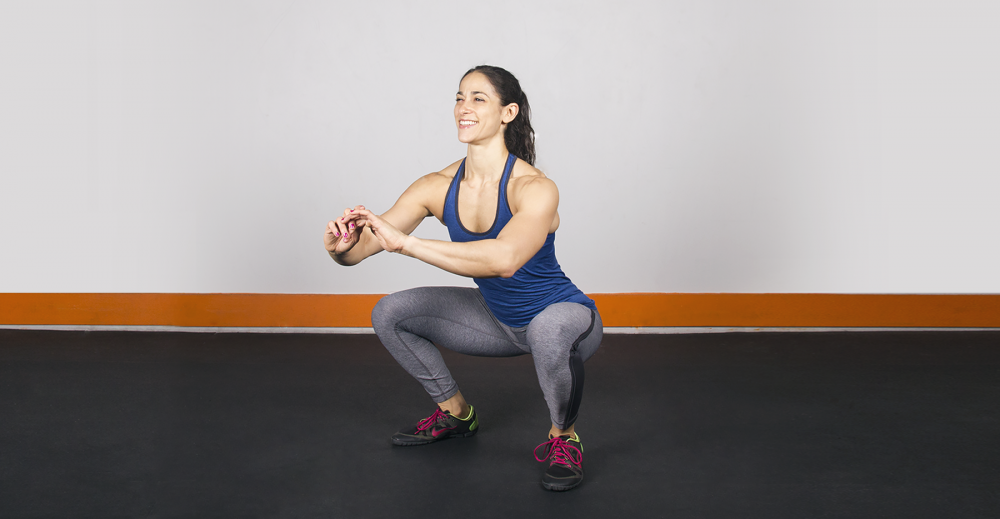

Your quadriceps or upper leg muscles are skeletal muscles. Simple squats, lunges and jumping jacks are great ways to strengthen your quads. Try starting with some back squats, split squats and goblet squats. If you have weights at home, try barbell or kettlebell squats.
Work on your obliques
Your external obliques are skeletal muscles located near your abs. Work on your lats with side planks or give yourself an extra challenge with side planks. Side bends, side kicks and wood choppers are also great ways to work these muscles.
Exercise your hamstrings.
Your hamstrings are skeletal muscles in the back of your legs. Hamstring curls are a great way to work these muscles, as are kettlebell and dumbbell deadlifts. Walking is another great way to strengthen your hamstrings.
Focus on your glutes.
Your glutes are skeletal muscles that cover your bottom. Strengthen your glutes with simple exercises like glute bridges or side squats. Bulgarian split squats are another great way to work your glutes.[16]
Strengthen your lats.
Your lats, or upper back muscles, are skeletal muscles. Pull-ups are a classic, easy exercise that really works your lats. Other great workouts are medicine ball crunches and bent-over barbell rows.
Fill your diet with protein.
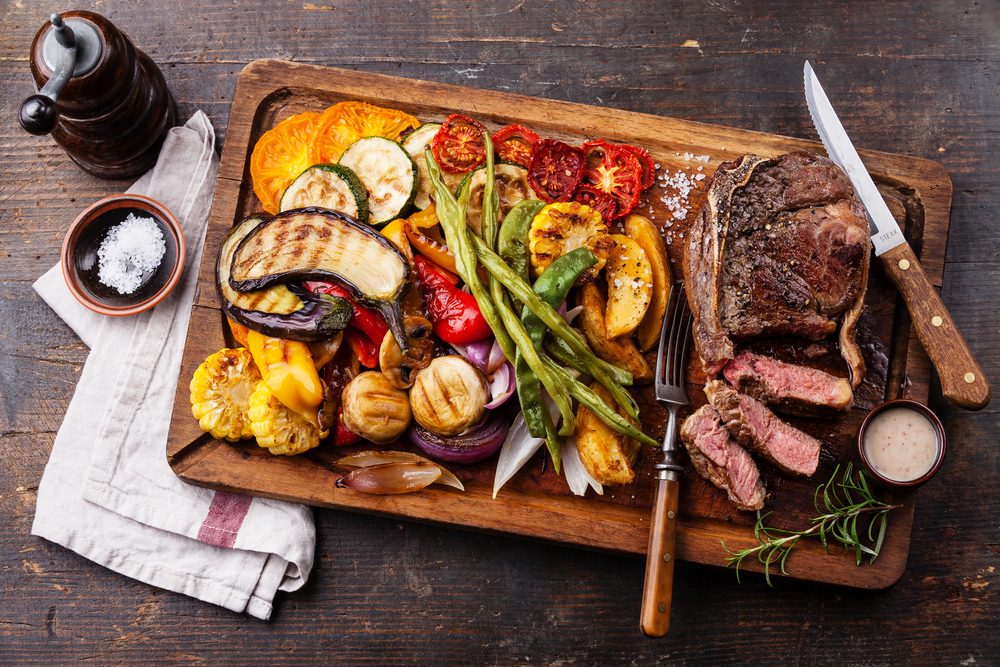

Eat 1.4 to 2 g of protein for every 1 kg (2.2 lb) you weigh. Foods rich in protein can help you build and maintain muscle. Lean meats, such as beef and pork, and poultry, such as chicken and turkey, are excellent sources of protein. Dairy products, fish, seafood, beans and nuts are also excellent sources of protein.
Schedule rest days

Your muscles grow when you rest, not when you exercise. a challenging weight training session increases protein storage for up to 48 hours immediately after exercise.
Increasing rather than just maintaining your skeletal muscle and improving your muscle quality will allow you to maintain movement and exercise and develop and improve it.
Without a doubt, exercise, adequate rest, and a balanced diet will help keep your muscles healthy for life.
Denial of responsibility
The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health care provider with any questions you may have about a medical condition.
