Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes of diabetes and how to prevent it is vital to managing and reducing its prevalence. This article examines the top 10 causes of diabetes and offers practical prevention tips.
Types of Diabetes

Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is one autoimmune condition where the body attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It often develops in childhood, but can appear at any age. Learn more about Type 1 Diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is more common and is usually associated with lifestyle factors. The body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough, leading to high blood sugar levels. Medicines such as Rybelsus 3 mg💊(semaglutide) can be used to help manage blood sugar levels by boosting the body’s natural insulin secretion and improving blood sugar control.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. It requires careful management to ensure the health of both mother and baby.
1. Genetics and Family History


If diabetes runs in your family, you may have a higher risk of developing the condition. While you can’t change your genetics, knowing your family history can help you take preventative measures.
Prevention tip: Maintain a healthy lifestyle, monitor your blood sugar levels regularly and consult your doctor for personalized advice.
2. Obesity


Excess body weight, especially around the belly, significantly increases the causes of diabetes. Fat cells, especially visceral fat, can cause insulin resistance.
Prevention tip: Aim for a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables and lean proteins. Regular physical activity is also essential. Set realistic weight loss goals and track your progress.
3. Physical Inactivity


A sedentary lifestyle is one of the main causes of diabetes. Lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance.
Prevention tip: Incorporate 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as brisk walking or cycling, into your daily routine. Think of activities you enjoy to make exercise a regular part of your life.
4. Poor Nutrition


Eating a diet high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and processed foods can increase your risk of diabetes. These foods can lead to weight gain and poor blood sugar control.
Prevention tip: Focus on a diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats. Limit sugary drinks and processed foods. Choose water, herbal teas and natural snacks.
5. Age


As we age, the risk of developing diabetes increases. This is partly due to a natural decrease in insulin production and increased insulin resistance.
Prevention tip: Stay active and maintain a healthy diet as you age. Regular checkups with your healthcare provider can help monitor and manage your risk.
6. High blood pressure
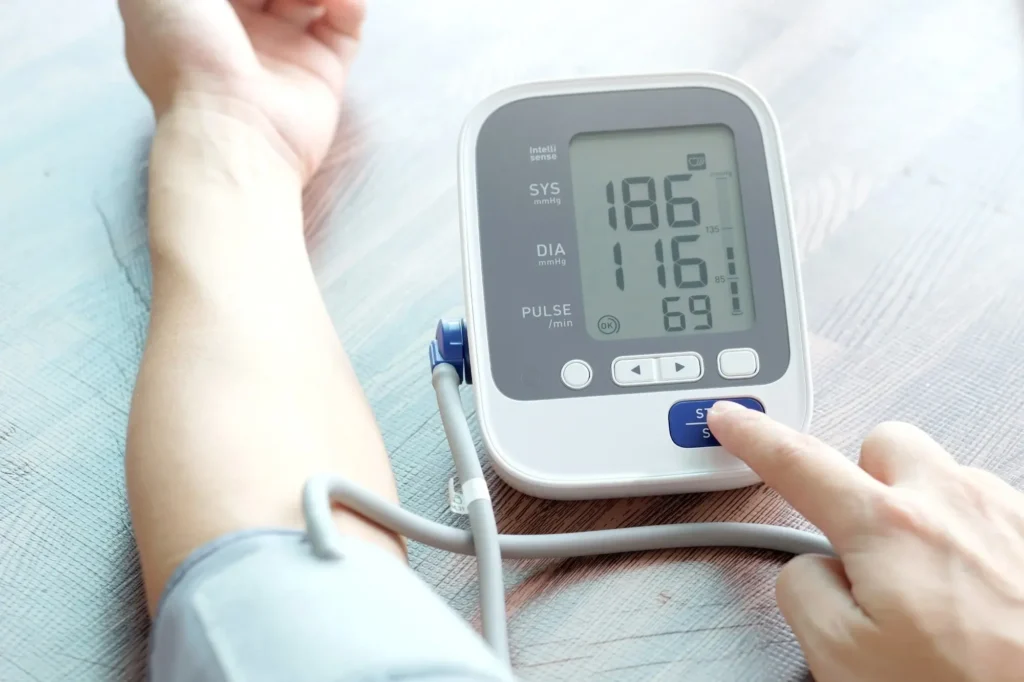

Hypertension is closely related to diabetes. High blood pressure can damage blood vessels and contribute to insulin resistance.
Prevention tip: Monitor your blood pressure regularly. Reduce sodium intake, maintain a healthy weight and engage in regular physical activity.
7. High cholesterol levels


Elevated cholesterol levels, especially LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, can increase the risk of developing diabetes. High cholesterol can lead to atherosclerosis, which can affect blood flow and insulin delivery.
Prevention tip: Eat a heart-healthy diet, avoid trans fats and include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Regular exercise and medications, if prescribed, can help manage cholesterol levels.
8. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)


PCOS is a condition in women characterized by irregular menstrual periods, excessive hair growth and obesity. It is associated with insulin resistance, which can increase the risk of diabetes.
Prevention tip: Manage your weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise. Medicines and lifestyle changes can help regulate menstrual cycles and insulin levels.
9. Hormonal Changes


Certain hormonal conditions, such as Cushing’s syndrome and hyperthyroidism, can increase the risk of diabetes. These conditions affect the body’s ability to use insulin properly.
Prevention tip: To Manage hormonal changes and reduce your risk of diabetes, it is important to have regular health checks to monitor your hormone levels, maintain a healthy diet and maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
10. Gestational diabetes


Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Prevention tip: Women with a history of gestational diabetes should have regular checkups after pregnancy and adopt a healthy lifestyle to manage their risk.
conclusion
Understanding the leading causes of diabetes and how to prevent it can significantly reduce your risk. By making healthy lifestyle choices and staying informed, you can manage or even prevent diabetes. Remember, it’s never too late to start making positive changes!
