In a recent review published in the journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine, The researchers reviewed the available literature on the role and mechanisms (molecular and pathological) by which cholesterol imbalances in the brain contribute to neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Huntington’s disease (HD), and Parkinson’s disease ( PD).
They review more than 80 publications for critical mechanisms, including synaptic dysfunctions, amyloid beta (Aβ) protein oligomers, protein clustering, and alterations of membrane structure and α-synuclein aggregation. Their findings suggest that altered cholesterol synthesis and metabolism are common features of most investigated neurodegenerative diseases. While cholesterol-lowering drugs can partially reduce the risk of these diseases, additional research is needed to develop future targeted pharmacological interventions against these conditions.
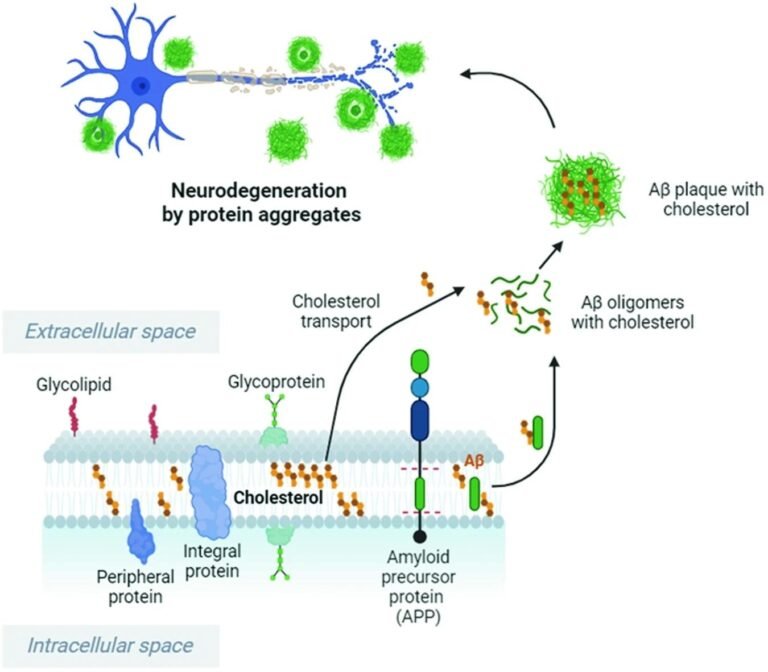
Cholesterol enhances and accelerates the cleavage of APP by Bace1, leading to increased oligomeric Aβ and plaque formation. Cholesterol binds to Aβ and increases the resistance of Aβ fibrils and oligomers to degradation. Cholesterol imbalance and high extracellular cholesterol levels can stimulate the production and accumulation of Aβ peptides, which cause the formation and accumulation of Aβ oligomers in the brain, resulting in neuronal damage. This image was created with BioRender.com. Study: Cholesterol imbalance and neurotransmission defects in neurodegeneration.
Record
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in the cell membranes of all human cells. It plays an integral role in neuronal signaling and synaptic connections, especially in the brain. Specifically, the brain contains between 20-25% of all the body’s cholesterol stores, making it the organ with the highest concentration of cholesterol in the human body. Interestingly, peripheral cholesterol (cholesterol absorbed from the diet circulating in the bloodstream) is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Consequently, almost all of the brain’s cholesterol stores are derived from de-novo synthesis (in glia and neurons).
As people age, the efficiency of cholesterol-synthesizing glia and neurons declines, depleting their brain’s cholesterol stores and resulting in reduced synaptic plasticity and overall loss of synaptic function. These losses have been suggested to be major contributors to increased risks of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Huntington’s disease (HD), and Parkinson’s disease (PD). Unfortunately, the molecular and pathological mechanisms underlying these observations remain poorly understood.
About the study
The present study gathers and reviews more than 80 cholesterol-related publications to elucidate four key molecular mechanisms underpinning associations between cholesterol imbalances and subsequent adverse neurodegenerative outcomes. These mechanisms include: 1. Synaptic dysfunction, 2. Amyloid beta (Aβ) aggregation, 3. Protein aggregation, alterations in membrane structure, and 4. α-synuclein (α-syn) aggregation.
Molecular mechanisms
1. Synaptic dysfunction – Cholesterol has been observed to make up to 80% of the plasma membrane of synapses and is essential for both their formation and function. Research has indicated that cholesterol imbalances can significantly alter the ability of synapses to effectively share neurotransmissions, ultimately resulting in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecular models have revealed that cholesterol imbalances adversely affect Ca2+-dependent vesicle fusion by altering membrane elasticity. In extreme cases, this can lead to significant unwanted changes in membrane bending and curvature, increasing the energy required for membrane/vesicle fusion and reducing neurotransmission.
2. Aβ protein oligomers – Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is converted to Aβ protein by enzymatic cleavage catalyzed by Bace1 β-secretase. Given its integral role in protein aggregation and folding, successful conversion of APP protein to Aβ protein relies on normal brain cholesterol levels, with changes in the latter observed to cause misfolding of the former. Misfolding of the Aβ protein results in the formation of Aβ plaques, the accumulation of which is a hallmark of AD pathology. “Cholesterol imbalance and elevated extracellular cholesterol levels can promote the production and accumulation of Aβ peptides, which cause the formation of Aβ oligomers in the brain, thereby contributing to neuronal damage and cognitive decline.” Tau aggregation (specifically, hyperphosphorylated tau), another hallmark of AD pathology, is also dependent on cholesterol concentrations, given the membrane curvature properties of the latter. Recent research has clarified that cholesterol-free membranes cannot form tau fibrils, whereas cholesterol-containing membranes affect tau fibril formation that depends on cholesterol concentration and relative membrane curvature. Unfortunately, the effects of cholesterol on tau nucleation remain poorly studied and currently unknown.
3. Protein cluster and membrane structure – Cholesterol has been shown to play an integral role in regulating normal membrane curvature, structure and fluidity. Curvature and deformation are essential for vesicle function and stabilization of fusion pores, allowing diffusion of neurotransmitters into the central nervous system. Recent research has further revealed that cholesterol is critical for protein clustering and intracellular organization of soluble proteins of the N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor receptor (SNARE). Communication between different SNARE proteins (syntaxin-1A, SNAP-25 and VAMP-2) together comprises the SNARE core complex, which mediates vesicle fusion and, in turn, neurotransmitter release within a synapse.
4. aggregation a-syn – The genesis and progression of PD is characterized by the accumulation of unfolded α-syn proteins in Lewy bodies (LBs). The mechanistic basis of this process is a consequence of α-syn binding to membrane lipids. Imbalanced cholesterol accelerates α-syn accumulation and LB formation, increasing the risk of PD.
Future therapeutic interventions
The most basic family of neural proteins involved in normal cholesterol transport and metabolism is the apolipoprotein E (ApoE) family (ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4). ApoE4 has also been identified as a critical risk factor in late-onset AD. Unfortunately, the molecular contributions of the ApoE family are poorly understood and require further investigation. However, given the role and importance of ApoE4 in both cholesterol homeostasis and AD pathology, it may be highlighted as a target for clinical trials and future pharmacological interventions.
conclusions
The mechanistic basis of cholesterol in various neurodegenerative diseases is context dependent. However, the present study highlights how imbalances in cholesterol levels, especially in the brain, can increase the risk of these diseases and suggests possible strategies for their management.
“While cholesterol-lowering drugs, eg, statins, have shown some potential in reducing the risk of certain neurodegenerative diseases, further research is needed to fully understand the role of cholesterol and develop targeted therapeutic interventions.”