Skin conditions, ranging from minor irritations to serious disorders, affect individuals significantly. This guide covers various skin conditions, focusing on symptoms, causes and developments in treatment. Understanding these conditions is vital, as environmental factors and lifestyle choices play a key role in skin health. We aim to offer information on caring for and protecting your skin through a mix of traditional and modern treatments, emphasizing the importance of understanding skin conditions and treatments.
Skin problems affect not only the physical appearance but also have psychological effects. With advances such as personalized medicine and biologic therapies, dermatology is becoming more tailored and efficient. In addition, integrative care, combining medical and holistic practices such as nutrition and stress management, provides a comprehensive approach to maintaining skin health, emphasizing the types of skin treatments available.
Common skin conditions:
Acne: Acne, a widespread skin problem, is often aggravated by hormonal changes, stress and dietary factors. While traditional treatments focus on topical and oral medications, recent research highlights the importance of a holistic approach, including dietary modifications and stress management techniques. Understanding the underlying causes and preventive measures are as vital as the treatment, making acne management more effective and sustainable. This highlights the connection between common skin conditions and treatments.
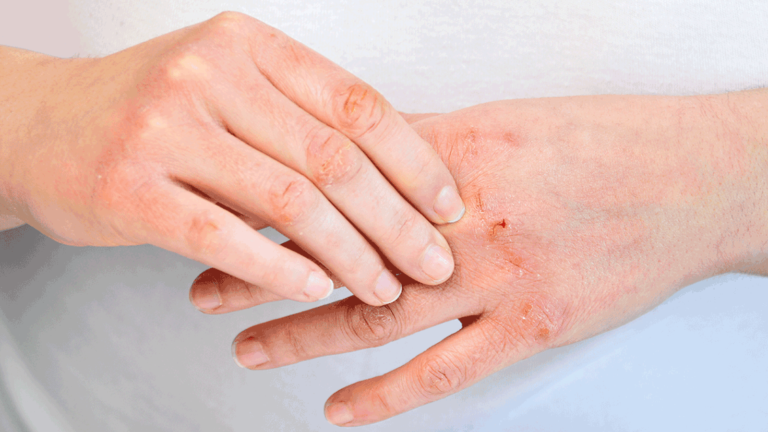
Eczema (Dermatitis): The unpredictable nature of eczema, often influenced by environmental factors and stress, requires a multifaceted therapeutic approach. In addition to medical treatments, understanding its role protection of the skin barrier and environmental control can significantly relieve symptoms. Recent advances in eczema care emphasize the importance of a preventive and preventative strategy for managing this condition, presenting different types of skin conditions.
Psoriasis: Psoriasis, beyond its physical manifestations, can have profound psychological effects. Current therapeutic strategies focus not only on symptom relief but also on improving overall quality of life. Research into genetic factors and immune system regulation has opened new avenues for more targeted and effective treatments for psoriasis, improving our understanding of skin diseases and treatments.
Rosacea: Rosacea, a condition that is often confused with other skin problems, requires a delicate understanding for effective treatment. Recent studies have shed light on the triggers and physiological processes behind rosacea, leading to more personalized and effective treatment plans. This includes a combination of topical treatments, lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, laser therapy, reflecting the variety of treatments and skin types.
Urticaria (hives): Sudden onset of urticaria requires understanding allergic reactions and avoiding triggering. While antihistamines remain the mainstay of treatment, ongoing research into immune response mechanisms offers hope for more targeted therapies in the future, aligned with the concept of skin diseases and treatments.

Rare skin diseases:
- Epidermolysis bullosa (EB):
The complexity of EB requires a multidisciplinary approach, including wound care, pain management and nutritional support. Emerging therapies, including gene therapy and stem cell research, offer hope for more effective management and possible treatments in the future, aligned with ongoing efforts to understand skin diseases and their treatments.
The rapid and aggressive nature of necrotizing fasciitis requires immediate medical intervention. Research into early detection methods and innovative antibiotic treatments is vital to improving survival rates and outcomes for affected individuals, underscoring continued progress in understanding skin conditions and treatments.
- Natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments:
In the area of skin health, the role of natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments cannot be overstated. Adopting a lifestyle that promotes skin health, including stress reduction, dietary adjustments and environmental awareness, is fundamental. These strategies, when combined with medical treatments, offer a holistic approach to skin disease management, emphasizing prevention and overall wellness.
Effect of environmental factors on skin health:
Environmental factors such as pollution, climate and exposure to UV radiation have significant effects on skin health. Pollution, especially in urban areas, exposes the skin to a variety of harmful substances, including particulate matter, heavy metals and gases, which can lead to skin ageing, acne and other dermatological problems. Climatic factors such as humidity and temperature affect skin moisture levels and barrier function. For example, environments with low humidity can cause dryness and worsen conditions such as eczema, while high humidity can worsen acne.
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a major cause of skin aging and skin cancer. It is essential to protect the skin from UV damage by using sunscreens with appropriate SPF levels, wearing protective clothing and avoiding excessive sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
To mitigate these environmental effects, individuals can use skin care products with antioxidants to fight free radical damage, maintain a regular cleansing routine to remove pollutants, and use humidifiers to manage indoor air quality. air. Regular skin checks can also help in early detection of any adverse effects caused by environmental factors.
The role of nutrition in skin care:

Diet plays a key role in maintaining healthy skin. Vitamins, minerals and antioxidants in food can contribute to the health and appearance of skin. For example, vitamin C is known for its role in collagen production and skin repair, while vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect the skin from oxidative stress. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, flaxseeds and walnuts, are beneficial in managing conditions such as psoriasis and eczema due to their anti-inflammatory properties.
Hydration is also critical to skin health. Adequate water intake helps maintain skin elasticity and moisture barrier. Diets rich in fruits and vegetables provide hydration and essential nutrients that support skin health.
The gut-skin axis is an emerging area of research, suggesting a close relationship between gut health and skin disease. Probiotics and a balanced diet can support gut health, potentially reducing inflammation and improving conditions such as acne and eczema.
It is important to note that while diet and environmental factors play a role in skin health, they are not a substitute for medical treatments for skin conditions. A holistic approach that combines medical advice, skin care routines, environmental adaptations and nutritional practices can lead to better management of skin conditions and overall skin health.
Navigating the complexities of skin conditions requires a balance of medical expertise, lifestyle adjustments, and an understanding of the latest research. Each person’s journey with their skin condition is unique and requires individualized care and treatment plans. By embracing both traditional and innovative treatment methods, individuals can achieve not only symptom relief but also a deeper sense of well-being and self-confidence.