Scientists at the National Central University of Taiwan investigated the relationship between skin microflora and cognitive brain functions using electroencephalography and machine learning methods.
The study is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Study: Exploring the potential relationship between the skin microbiome and cognitive brain functions: a pilot EEG study. Image credit: ART-ur / Shutterstock
Record
The human microbiota is defined as a vast pool of heterogeneous microorganisms found primarily in the gastrointestinal tract (gut microbiota) and skin (skin microbiota).
The gut microbiota is known to play essential roles in regulating many physiological functions by producing short-chain fatty acids and other metabolites. In addition to maintaining intestinal homeostasis and regulating metabolic and immune functions, the gut microbiota plays a critical role in regulating vital brain functions through the bidirectional gut-brain axis.
Like the gastrointestinal tract, skin-inhabiting microorganisms are vital for maintaining skin homeostasis, preventing foreign invaders (pathogens and chemicals) from entering the body, regulating immune functions, and degrading natural products. These functions are exerted by short-chain fatty acids produced by the microflora of the skin.
The growth of bacteria on human skin depends on several factors, such as the skin microenvironment, age, sebum level, hormonal level and sweat production. An imbalance in the microbial composition and diversity of the skin (dysbiosis) can lead to various skin conditions, such as atopic dermatitis, wounds, psoriasis, acne vulgaris, diabetic foot ulcer or Pityriasis Versicolor.
In this study, scientists evaluated interactions between skin microbiota and brain signals related to cognition in healthy individuals.
Study design
The study was conducted on a total of 20 healthy subjects. Each participant’s level of attention (cognitive function) was measured using a classical monosphere task involving an odd and a standard stimulus with different frequencies presented in a random order.
Each participant’s electrical brain activities were measured during the oddball task using electroencephalography (EEG) under three different conditions of bacterial population manipulation on the participant’s forehead.
Bacterial populations were subjected to alcohol, glycerin and water manipulations to investigate the effect of skin microbiota on brain cognitive functions. Alcohol, glycerin, and water manipulations were applied to eliminate skin bacteria, increase skin bacterial growth, and mimic natural skin bacterial growth.
EEG changes (event-related potentials, ERPs) were analyzed using statistical and machine learning methods to detect the impact of skin microbiota manipulations on attention-related brain activities.
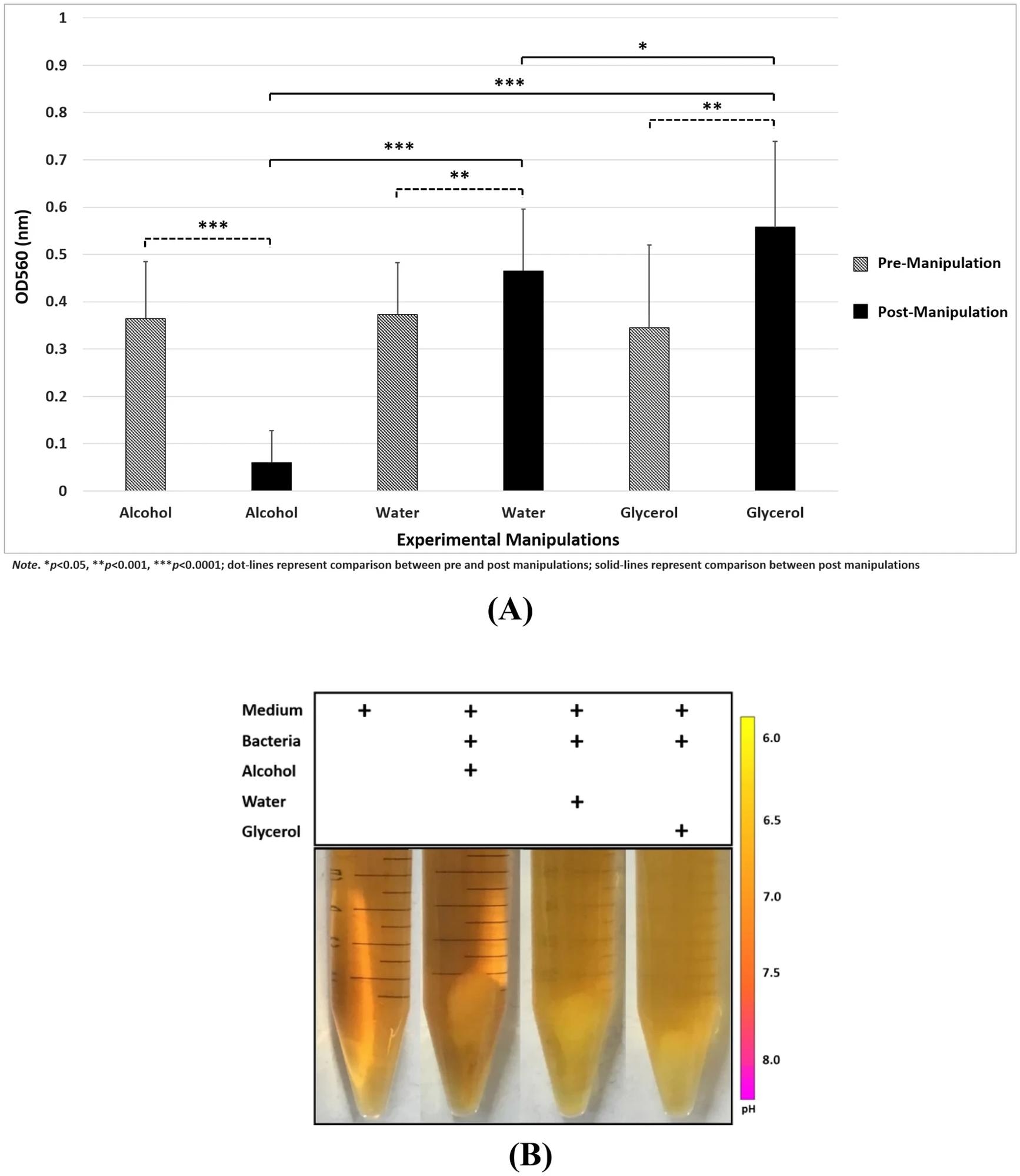 (ONE) Significant effects of the experimental manipulations on the bacterial population. (si) Color changes after experimental manipulations indicated bacterial fermentation.
(ONE) Significant effects of the experimental manipulations on the bacterial population. (si) Color changes after experimental manipulations indicated bacterial fermentation.
Important observations
Optical density measurements of bacterial populations under three experimental manipulations revealed significantly increased bacterial growth under water and glycerin conditions compared to that under alcohol conditions.
Participants’ levels of cognitive processes were determined by measuring ERPs of N200 (negative peak at 200 milliseconds) and P300 (a positive peal at 300 milliseconds) in response to experimental stimuli.
According to the available literature, increased N200 amplitudes are indicative of selective allocation of spatial attention, novelty or mismatch detection, and cognitive control. Similarly, enhanced P300 amplitudes are associated with selective attention.
Effective implementation of the oddball task was determined by examining ERPs under the water manipulation condition. Findings revealed significantly higher P300 amplitudes in the central-parietal region in response to the monosphere stimulus compared to that for the standard stimulus. This indicates efficient execution of the work.
ERP measurements under experimental manipulations revealed that alcohol manipulation (bacteria removal) induces a significant induction in P300 amplitudes in response to a single-shot stimulus alone compared to water and glycerol conditions (increased bacterial growth). These observations suggest that removing bacteria from the skin increases participants’ level of attention.
However, despite significant variation in bacterial growth under water and glycerol conditions, these two experimental manipulations observed no significant differences in P300 amplitudes.
This observation indicates that the effect of skin bacterial population on the P300 signal is not proportional to the number of bacteria. Conversely, it can be assumed that the increased bacterial population does not degrade brain signals.
Based on pre-existing evidence, the scientists hypothesized that glycerin may increase the growth of certain but not all bacteria, and that not all bacteria can affect brain signals. They further hypothesized that the decrease in P300 amplitude under water and glycerol conditions may be due to an imbalance in the concentration of short-chain fatty acids in the skin due to bacterial overgrowth.
Important study
The study finds that removing the skin’s bacterial population can significantly increase P300 amplitudes along the midline channels, suggesting a significant improvement in attention level.
The study also finds that machine learning classifiers can separate each experimental manipulation using EEG data with greater than 88% accuracy.