A new meta-analysis finds that “laughing gas” can relieve symptoms of depression within hours, highlighting a fast-acting antidepressant approach that may work best when repeated carefully rather than just once.
Study: Nitric oxide for the treatment of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Image credit: mazur serhiy UA / Shutterstock
In a recent review published in the journal eBioMedicineresearchers combined data from protocol documents, clinical trials, and exploratory studies to evaluate evidence regarding the effectiveness of nitrous oxide for the treatment of depression.
They concluded that within hours of administration, nitrous oxide can produce a rapid antidepressant effect with generally transient, dose-dependent side effects. However, further research is needed to confirm these findings.
Growing interest in fast-acting depression treatments
Depression affects more than 300 million people worldwide. Its causes include complex interactions between environmental, biological, and psychological systems that disrupt stress-regulatory pathways and neural circuits.
Standard antidepressants remain insufficient for many patients. This has intensified research focus on faster-acting treatments that can support people with depression, particularly those experiencing treatment-resistant depression.
Mechanistic rationale of nitric oxide as an antidepressant
Increasing research has turned to the glutamatergic system, prompted in part by the rapid-acting antidepressant effects of ketamine. Nitric oxide, an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist widely used as an anesthetic, has shown similar rapid-acting benefits accompanied by short-lived, dose-dependent side effects.
Its actions include modulating glutamate signaling, altering activity within the default mode network, and influencing the dopamine and opioid systems. These mechanisms have positioned nitrous oxide as a promising candidate for further investigation as a novel antidepressant.
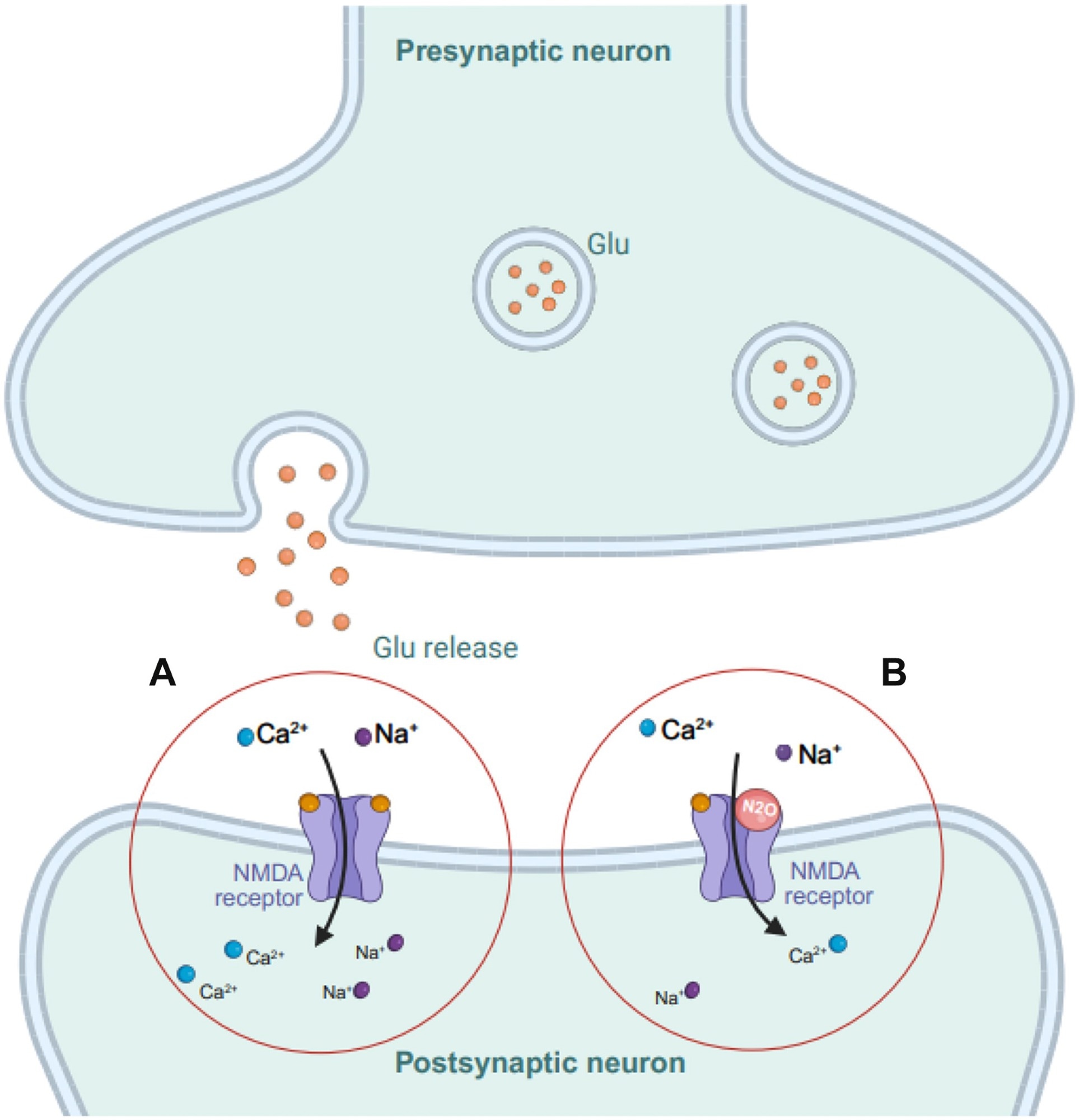
Mechanism of action of nitric oxide (N2O) in modulating NMDA receptor activity. In the normal state (A), glutamate (glu) binds to NMDA receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, causing calcium (Ca2+) and sodium (Na+) ion influx, which causes excitatory signaling. In B) N2O partially blocks NMDA receptors, inhibiting glutamate binding and preventing Na+ and Ca2+ influx, thereby reducing excitatory signaling. This ion regulation affects the excitatory and inhibitory balance in the central nervous system and is involved in depression. Image created with BioRender. Gill, K. (2025) https://BioRender.com/a87q343.
Clinical evidence base for nitrous oxide
The review identified eleven eligible studies, including seven completed clinical trials, most of which were randomized controlled trials, and four published protocol papers. These studies represented early phase research conducted in Australia, Brazil, China and the United States.
Across all completed trials, a total of 247 participants were enrolled, including people with major depressive disorder, treatment-resistant depression or bipolar depression. Nitrous oxide was typically administered at concentrations of either 25% or 50%. It was administered via controlled inhalation for periods ranging from 20 to 60 minutes, either as a single treatment session or as repeated sessions scheduled weekly or biweekly, with most pooled efficacy estimates based primarily on 50% single-session protocols.
Rapid antidepressant effects from single doses
Overall, the studies showed that one session of nitrous oxide could rapidly reduce symptoms of depression, with detectable improvements within two hours of its administration.
In one of the first trials, scientists found that a 60-minute session of 50% nitrous oxide led to significantly lower depression scores compared to a placebo at both two and 24 hours. People who received the treatment were also more likely to experience significant improvement (20% vs. 5%), and some even went into remission within a day.
Another study reported similar results in people with treatment-resistant depression: symptoms improved within hours. However, the effect disappeared by one week. A third study found that nearly half of the participants were still showing improvement a week after just one treatment, especially those who responded strongly at first.
Results for bipolar depression were less consistent. In one study, both nitrous oxide and the comparator drug midazolam reduced symptoms. However, nitrous oxide helped more people get better within the first two hours. The study also suggested that people with certain blood flow patterns in the brain may be more likely to benefit, hinting at a possible biological marker for predicting treatment response.
Enhanced and sustained benefits with repeated doses
Studies that included multiple treatment sessions showed more substantial and more consistent improvements in depression symptoms. In all repeated-dose studies, the greatest improvements usually occurred within 24 to 48 hours after each treatment and accumulated over time.
For example, eight sessions over four weeks resulted in very high rates of improvement and remission compared to a placebo.
Another study found that both low-dose (25%) and high-dose (50%) nitrous oxide reduced symptoms over two weeks, although the higher dose was more effective. The lower dose, however, caused fewer side effects such as nausea and dizziness, suggesting that it may be a good compromise between efficacy and tolerability.
The most extensive study to date found that weekly sessions for four weeks led to steady, cumulative improvement. People who received nitrous oxide were more likely to go into remission in the first week than those who received a placebo, and the 50% dose again produced the strongest results.
Summary findings from the meta-analytic synthesis
When data from multiple trials were combined, nitrous oxide showed clear antidepressant effects both two hours and 24 hours after treatment. These early improvements were consistent across studies, with very low statistical heterogeneity.
However, the combined data showed no lasting benefits at one week, suggesting that the main effects are short-term unless treatments are repeated. Because only a small number of trials contributed to the pooled estimates, some asymmetry in the funnel plots suggests that publication bias cannot be excluded and blinding may have been incomplete in some trials, raising the possibility of effects of expected duration.
Overall conclusions and research gaps
Researchers have found that in a small number of early-phase trials, nitric oxide produces rapid, short-term antidepressant effects, with repeated doses extending both the magnitude and duration of benefits.
However, most studies were small early-phase trials with heterogeneous designs, limited long-term follow-up, and insufficient power to compare doses or fully identify prognostic factors. Differences in delivery systems, comparators and outcome measures also limit comparability. Safety data, although generally reassuring, remain incomplete for long-term or repeated use.
Overall, the evidence suggests that nitrous oxide is a fast-acting antidepressant candidate that is generally well tolerated, with higher rates of mild, transient side effects than placebo, but that larger, larger, and mechanistically informed trials are needed.
