A new systematic review reveals the nutrition and recovery strategies that help the triarrms to remain stronger, recover faster and reduce health risks, strengthen athletes and coaches with science -backed guidance for each race.
Review: Triathlon: Ergo Nutrition for training, competition and recovery. Credit Picture: Maridav / Shutterstock
In a recent systematic review published in the magazine NutrientsThe researchers systematically evaluated and compose the findings from an initial group of 1,628 studies, which eventually include 35 nutrition, completion and rehabilitation articles for the scientific optimization of the holistic performance of the triathletes. The review is registered with Prospero and adheres to Prisma’s guidelines, enhancing its methodological rigor. It highlights the unique metabolic and nutritional requirements of the sport, with the aim of providing coaches, clinics and athletes with the practical knowledge needed to preserve and promote optimal training, day -to -day performance and recovery.
The findings of the study reveal that the trio (both men and women, with women particularly vulnerable due to nutritional patterns and physiological agents) are in increased relative energy deficiency in the risk of sport (RED-S), emphasizing the importance of muscle balances, Triathlon’s requirements. Regularly monitoring the energy status under professional supervision and timely supplementation can help alleviate this risk, allowing tomorrow’s three -day trips to run, switch and swim faster and safer than ever.
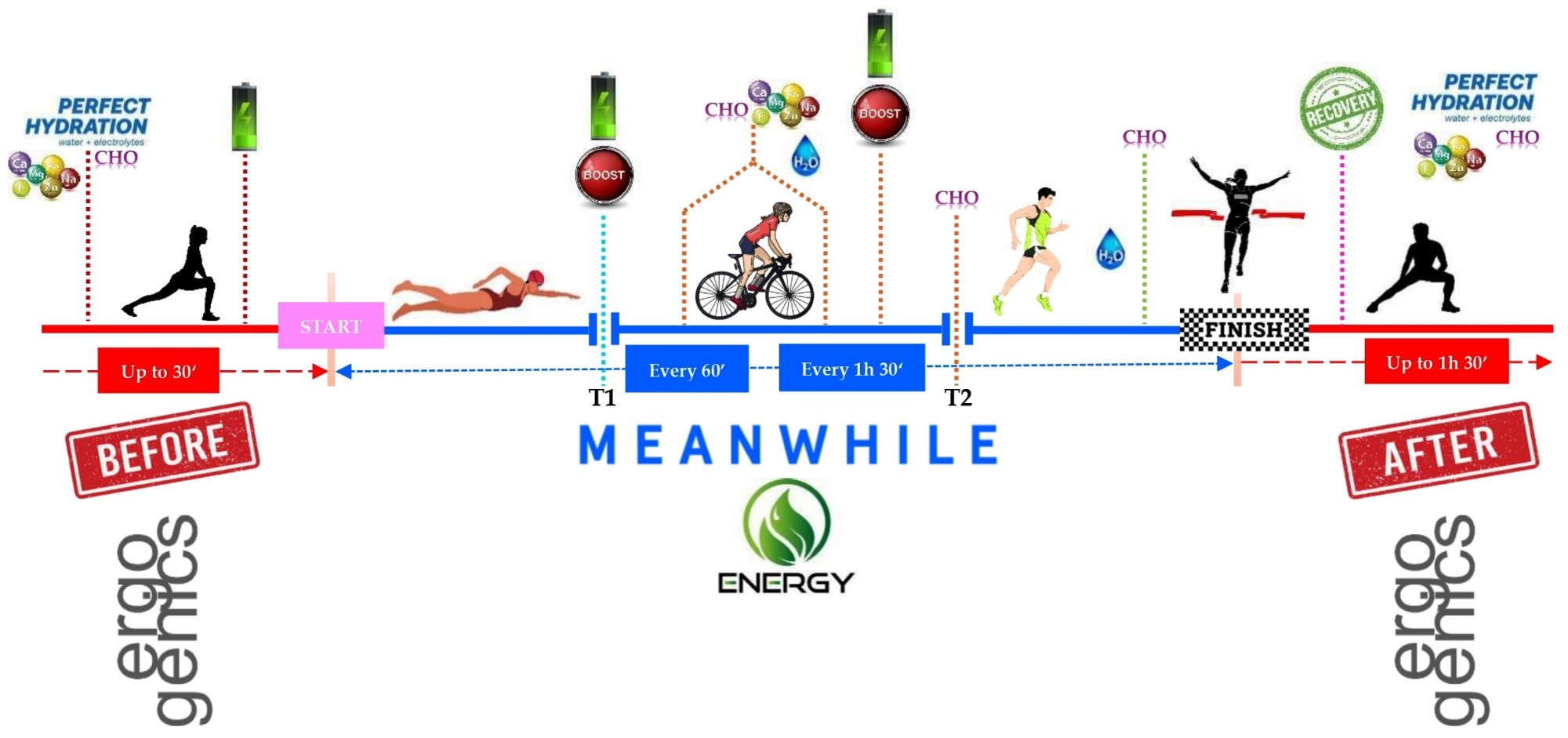 Possible diet strategy.
Possible diet strategy.
Background
‘Triathlon’ is a term umbrella for multi -disciplinary sporting events that combine running, cycling and swimming in a single race. The subtypes of the sport range from the relatively short “Super Sprint” (350 m swimming, 10 km, 2.5 km) in the exhaustive “Ironman” (3.86 km swimming, 180 km bike, 42.2.2 km.
Maximizing the performance of the triathlon, while minimizing injury, has unique nutritional and recovery. While several athletes take advantage of supplements (ergogenic and nutritional), misconceptions about their use and inadequate nutritional education between their triads and their coaches often lead to underlying or dyspressary results.
In -depth knowledge of the advantages and disadvantages of various nutritional practices (including the use of Ergonutrition and Supplement) and recovery methods would allow for the optimization of performance, allowing the trio to train and fight more effectively, while protecting themselves. prosperity.
For the study
This systematic review concentrates the current scientific literature that evaluates the diet and the recovery of the triathlon during training (pre-, intra- and after training) and periods of competition. Its aim is to enhance the well -being and performance of athletes, identifying the optimal triathlon support strategies and promoting issues for future research in sports nutrition.
The review complies with the preferred reference elements for systematic revisions and Post-analyzes guidelines. It utilizes the Picos design model for the study of PICOS comparators to determine the revision integration criteria. The study was selected through a custom search of 11 electronic databases: 1.
A successive sorting process (title, summary, full text) was used to select articles that: 1, which focused on three -number, 2, unauthorized study plans and 3. Studies included were categorized in nutrition studies and 2.
Exported review data included: 1. Study source, 2. Methods, 3. Sample, 4. Intervention details and 5. The quality of the data and the gaps of the literature were evaluated using the reference to observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) and Cochrane CoCchrane cooperation guidelines. Finally, the results of the basic variables (intake of carbohydrates and proteins, fluid balance, antioxidant use, supplementary efficacy) between cases and controls were evaluated.
Study findings
Initial database searches have identified 1,628 possible articles for inclusion in systematic review. The elimination of copies and the exception of the irrelevant and poor quality studies reduced this group of articles to 35 high quality versions. Descriptive and statistical analyzes have revealed that maintaining glycogen levels, especially through carbohydrate loading strategy, is the most critical variable that determines performance during training and competition.
The aspects of the thermoregulation and strength of the triathles are largely dependent on the optimal monitoring of hydration and electrolyte management (sodium level). Unfortunately, most included samples (three -ways) were observed to prove bad moisturizing practices during the competition phase, which increases the risk of dehydration and related performance and physiological degradation.
Specifically, the review identified significant nutritional deficits between the triads, especially during post -exercise rehabilitation practices, which resulted in the restoration of the muscle of the recovery phase, the reconstruction of glycogen and general well -being. Female participants were particularly vulnerable to energy deficits, some of which were associated with menstruation disorders and adverse psychological outcomes, such as relative energy deficiency in sports (RED-S) and injury.
However, all three-way, regardless of gender, are at risk of low energy availability (LEA) and RED-S, with unique dietary patterns (such as high fiber and plant diets), possibly increasing vulnerability, especially among women.
The review emphasizes the importance of applying specific recovery strategies, including adequate carbohydrates and intake of proteins after exercise, sufficient sleep, dipping cold water and use of compression clothing, to optimize recovery and minimize the risk of injury.
Encouraging, when used properly, eating and nutritional supplements (eg caffeine, krall oil, antioxidants, beetroot extracts, citrulline, branched chain amino acids (BCAAS) and probiotics were found to enhance recovery and performance. The elements are stronger to supplement carbohydrates, with emerging but less strong support for other types of supplement. Completion must always be personalized and supervised by qualified professionals. This review emphasizes the importance of scientifically up -to -date professional guidance, tailored to the athlete’s metabolic needs, previous training experience and the requirements of their Triathlon, to achieve optimal progress in this extremely demanding sport.
Conclusions
This review highlights the dietary priorities for the three -ways, emphasizing the importance of maintaining glycogen balance and sufficient hydration to achieve and maintain the performance of maximum in all phases of training and competition. It clarifies the significant normal benefits of supplements, but emphasizes the need for extensive training of athletes and strategic monitoring and planning to completely unlock their potential.
Integrated and personalized nutritional strategies, continuous training and careful recovery planning are essential to alleviating energy deficiencies, optimizing performance and promoting the health of athletes in the triathlon.
