Import
Have you ever had muscle tightening, limited movement or pain that never goes? If you have, you are probably talking welding. They are common between athletes and people who do similar repetitive physical activities. Knowing his science musculoskeletal welds It increases performance and helps prevent chronic pain.
This article dives deep into Muscle welding sciencetheir causes, the way they develop in athletes and effective treatments, including Physiotherapy for muscle adhesions; Deep tissue massage for adhesions; fascia release For muscle adhesions.
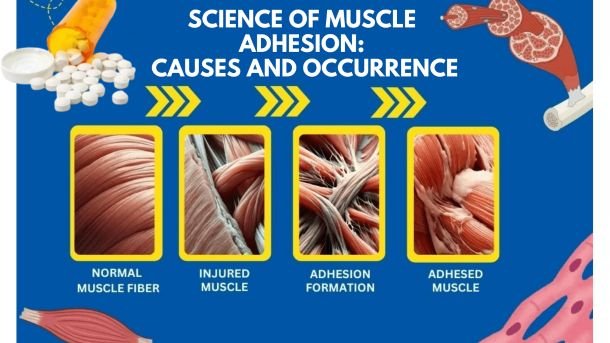
What are the muscle adhesions (myophilic)?
Muscle welds, also known as musculoskeletal welds They include fibrous zones that form between muscle fibers, fascia and connective tissue. They limit mobility, offer discomfort and reduce muscle function.
Muscle lentils stuck together prevent smooth movement and production chronic pain with welding. This condition gradually develops over time, causing flexibility and performance disorders within a person.
The science behind the formation of muscle adhesion
The human body is a complex structure consisting of muscles, tendons and fascia, working together to allow movement. However, injuries, excessive use or inactivity can lead to scar tissue in the muscleswhich restricts their physical function.
Its formation post-surgical muscle agreement and Prevention of adhesion after surgery It is also a crucial issue in rehabilitation science. These adhesions develop when the body tries to heal by creating excessive collagen, which then hardens in restrictive zones.
Understanding the anatomy of adhesions
FASCIA: The body’s invisible network
Fascia is a thin layer of connective tissue that surrounds the muscles, bones and organs. When healthy, it allows smooth movement. However, damage to the fascia can lead to musculoskeletal weldscausing stiffness and pain.
Scarring
The scar tissue is formed as part of the body’s natural therapeutic reaction. However chronic muscle adhesionslimiting flexibility and causing discomfort.
How do muscle fibers stick together?
When the muscles undergo anxiety or injury, micro-fractures occur. The body repairs these collagen tears, but if the healing process is incomplete or excessive, the collagens accumulate together, forming adhesions.
Poor attitude, excessive use or lack of mobility can accelerate the attachment process, leading to pain and motion restrictions.
How do muscle welds grow on athletes?
Athletes often push their bodies to the limit, making them particularly sensitive welding. Some common causes include:
- Repetitive anxiety in muscles
- Insufficient warm -up or cool routines
- Insufficient hydration and diet
- Muscle imbalances due to excessive training of certain groups
- Lack of appropriate recovery methods
The impact of adhesions on athletic performance
When adhesions are formed, they act as glue between muscle fibers, limiting movement and reducing elasticity. This can lead to:
- Reduced range of motion
- Increased risk of injury
- Reduced muscle strength
- Chronic discomfort and stiffness
Athletes with unprocessed chronic muscle adhesions It may notice a decrease in efficiency due to limited movement and muscle ineffectiveness.
Blocking muscle adhesions
While welding They are common, they can be avoided with the correct approach. Some effective prevention methods include:
- Regular exercises stretching and mobility
- Correct hydration to maintain muscle elasticity
- Balanced training programs to avoid muscle abuse
- Sufficient periods of rest and recovery
Welding treatment to athletes
Muscle welds can be a major obstacle to athletes, leading to limited movement, stiffness and discomfort. These adhesions occur when the fibrous tissues form between the muscles and the fascia, limiting flexibility and causing pain. Management of muscle adhesions requires a combination of treatments, self -care practices and, in some cases, drugs.
In this guide, we will explore the best ways to deal with and prevent muscle adhesions to help athletes recover faster and maintain top performance.
Routines before and after training to prevent welds
A well -structured exercise plan is essential for the prevention and management of muscle adhesions. Proper warm -up and cool routines can help keep the muscles flexible and reduce the risk of welding.
✔ Before training: Perform dynamic stretch exercises, such as foot swings, arm cycles and lunges to prepare muscle for activity.
✔ After Workouts: Participate in a static stretch to improve flexibility and reduce after exercise.
Sports Massage: A strong attachment treatment
Athletes often use deep web massage to break the fibrous tissue and improve muscle recovery. This technique:
✔ Deep muscle targeting layers for release of intensity and adhesions.
✔ Increases blood circulation, promoting faster healing.
✔ Reduces muscle stiffness and pain, improving flexibility.
Natural treatments to treat muscle adhesions
Many natural treatments can help manage muscle welding and support muscle recovery. Here are some effective methods:
Massage treatment
✔ Pressure application in affected areas increases blood flow and breaks the adhesions.
✔ Use essential oils such as mint or eucalyptus for additional relaxation.
Stretching exercises
✔ Focus on yoga or mobility exercises to release muscle tightening.
✔ Integrate the PNF (proprietary neuromuscular facility) extending for deeper tissue release.
Hydrotherapy (water treatment)
✔ hot water baths, locomotive and contrast treatment (sinking with hot and cold water) help to relax the muscles and improve flexibility.
✔ Swimming is an excellent low -impact training that helps mobility.
Herbal remedies
✔ Aloe vera, turmeric and ginger have anti -inflammatory properties that help reduce adhesions and muscle pain.
✔ Think about drinking turmeric tea or using a ginger compression for relief.
Diet for muscle recovery
✔ A diet of nutritional density plays a key role in reducing inflammation and supporting healing.
✔ Include:
Fresh fruits and vegetables
Lean protein
Omega-3 fatty acids
When to consider muscle relaxing drugs
If natural treatments and treatments do not provide relief, muscle relaxing drugs can help. These can relieve pain, reduce muscle stiffness and improve mobility.
✔ Pain o soma 500mg – It helps to relax the muscles and relieve the pain caused by adhesions.
✔ Ibuprofen – Reduces inflammation and hassle.
✔ Soma boost 750mg – Provides stronger muscle relaxation for severe cases.
 |  |
Conclusion: Achieving maximum performance through attachment management
Understanding and management welding is essential for maintaining maximum physical performance. Incorporating Stretching for muscle adhesions; Deep tissue massage for adhesions; Physiotherapy for muscle adhesionsAthletes can prevent long -term complications.
Treating adhesions early can significantly improve mobility, reduce pain and enhance sports performance, making it vital to integrate adhesion management to regular fitness routines.
Frequently questions
1 Can muscle adhesions leave on their own?
In mild cases, appropriate stretching and mobility exercises can help reduce welding. However, chronic adhesions often require targeted treatments such as Deep tissue massage for adhesions and Physiotherapy for muscle adhesions.
2. How can I prevent muscle adhesions after surgery?
To minimize post-surgical muscle concentrationIt is necessary to follow Prevention of adhesion after surgery Protocols, which include mobility exercises, proper hydration and postoperative physiotherapy.
3. Is deep tissue massage effective for splitting muscle welds?
Yes, Deep tissue massage for adhesions It helps to break down scar tissue, improve circulation and restore muscle function, making it extremely effective treatment option.
4. How long does it take to recover from muscle adhesions?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity. Small adhesions can be improved within a few weeks with consistent treatment, while the most serious cases may require months Physiotherapy for muscle adhesions.
5. What is the best way to treat chronic muscle welds?
A combination Release of fascia for muscle adhesions; Stretching for muscle adhesions; Physiotherapy for muscle adhesions It is the best approach for long -term relief.