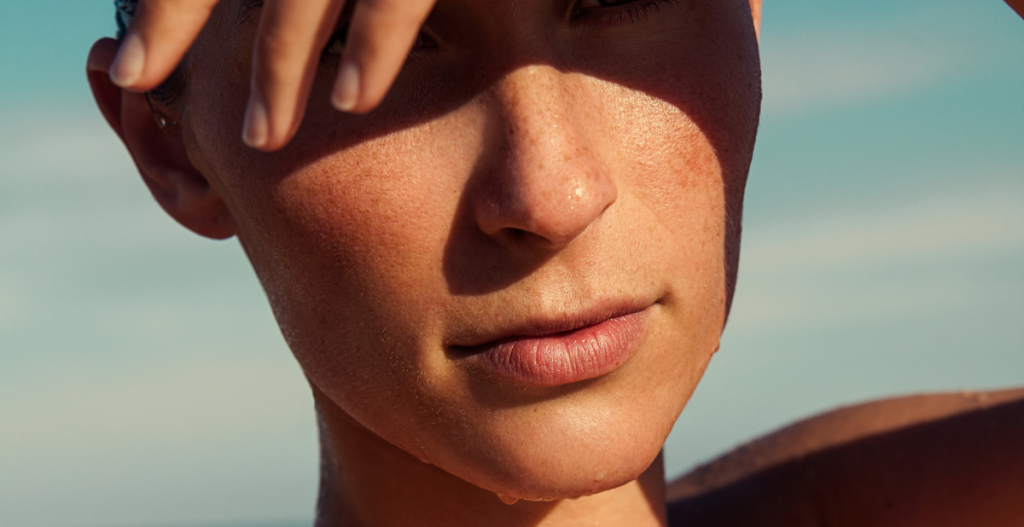
As the years go by, many of us avoid rejecting the sun. We return to hats and large coverage, worshiping the sunscreen wide range over the bronze. And rightly so, knowing that causes of exposure to the sun up to 80% of visible signs of aging skin.
But the sun is not a public enemy number one. The benefits of health keep us on and the effects that enhance the mood give us this End-summer-sensation We know and love. So if you are curious about how to enjoy the sun while protecting your skin, Learning for different types of solar and ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the key.
Let us dive with the help of one of our favorite experts, the special Isdin Medical Affairs Chiyoung Kang Park.
What is the solar spectrum?
The sun plays a vital role in our health, contributing to our mental well -being and helping our body produce vitamin D. but it also emits something called electromagnetic radiation. While some of them are absorbed, scattered and reflected before they reach Earth, the radiation we reach is called Solar spectrum.
The solar spectrum consists of various types of radiation, grouped by their electromagnetic frequencies. You have probably heard of some, such as Ultraviolet A (UVA) and Ultraviolet B (UVB). But as Kang states, “visible blue light and infrared radiation can also affect the way you appear and feels your skin.”
This spectrum ranges from the most active rays (ultraviolet) at least (infrared). Let’s take a look at how each of them affects your skin.
What is the difference between UVA & UVB radiation?
UVB radiation
Responsible for summer tanning lines, these high -energy rays mainly affect the external The layer of your skin. The UVB exposure depends on the time of day, position and weather – but it can even happen on cloudy days.
“UVB radiation is a key symbolist in short -term skin damage, such as sunburn,” Kang explains. “And while our body has antioxidant systems that help repair damage, frequent burns can weaken the ability of the skin to regenerate – increasing the risk of skin cancer.”
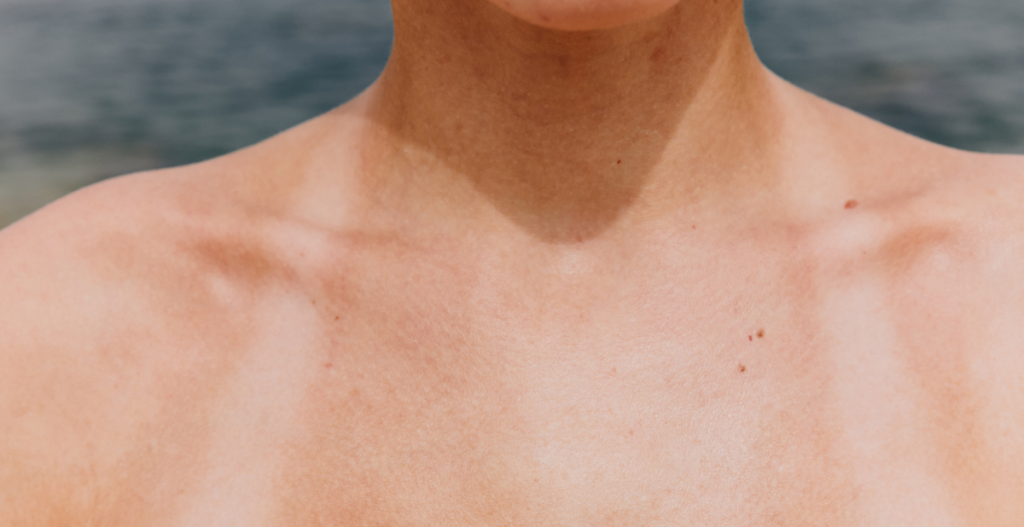
UVB radiation sheet
Main skin concern: Sunburn and their connection to skin cancer
Where does the report happen? Outdoors all year round, although levels vary according to climate and season
Extra credit: SPF or sun protection factor specifically refers to UVB protection. Dermatologists recommend Choosing SPF 30 or higher.
UVA radiation
On the other hand, UVA rays are longer wavelength and reach deeper into the skin. “UVA radiation contributes to long -term lesions such as photography and skin cancer,” says Kang. “It can also lead to solar allergies and some immunomodulations.”
Unlike UVB, UVA rays pass through clouds and glass – which means you are exposed even when driving or working indoors near windows.

UVA radiation sheet
Main skin concern: Signs of aging skin, sun allergies and skin cancer
Where does the report happen? Indoors and outdoors, all year long
Extra credit: Choose the sunscreen wide range – which means that it meets FDA standards for UVA protection.
Beyond UV: Other types of solar radiation
Solar blue light
High -energy visible blue light helps us to see the world around us literally. But research shows That it can also contribute to visible changes in the skin – especially to people with deeper skin tones.
“Solar blue light has been linked to heterogeneous coloring. And when combined with UV radiation, it can have a complex effect,” Kang said.

Scientific projector: People with deeper skin tones are more drastic in blue-immeasurable light. This light can activate the skin to produce more pigment, although it is less likely to burn. This means that the skin with a higher photocopy is uniquely sensitive to coloring worries.
Solar blue Luminaire
Main skin concern: Dark spots and heterogeneous coloring
Where does the report happen? Indoors and outdoors, all year long
Extra credit: Solar blue light is 100 to 1000 times more intense than blue light than artificial sources – increasing your sunscreen Use priority over the cutting season.
Infrared radiation
Infrared-A (IR-A) is different from ultraviolet radiation in a few ways. The most remarkable? Of warmer. While we cannot feel ultraviolet radiation, our skin absorbs the IR-A rays from the sun, causing this warm, sunny feeling. It is even used in some treatments to relieve muscle intensity.
But infrared radiation can also accentuate the skin. “Although it is the least active sunlight, IR-A rays can penetrate the skin and cause oxidative stress, especially when combined with UV rays,” Kang explains. The result? Wrinkles, loss of elasticity and dark spots – otherwise known as signs of photography.

Infrared sheet
Main skin concern: Strengthening the signs of aging of the skin
Where is the infrared exposure? Indoors and outdoors
Extra credit: Infrared or heat exposure is just one of the many exposure factors, such as pollution or stress, that affect skin health and appearance over time.
Are you worried about blue light or infrared? Turn to a sunscreen designed to provide extra defense.
Only the frequently questions
Is there a relationship between UV radiation and skin color?
Everyone is influenced by UV radiation, regardless of the tone of their skin. And these results can include skin cancer – making it extremely important to use proper sun protection every day.
Some people may also be at greater risk for ultraviolet -related damage, especially if:
- Have lighter skin tones
- Had repeated the sunburn during childhood
- Have used tanning beds
- Do you have a family history of skin cancer
- Is over 50 years of age
- Use medicines or products that increase sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation
How do melanocytes help protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation?
Your skin is trying to protect you from the rays of the sun. Skin cells called melanocytes react to sunlight (mainly UVA rays and blue sunlight) increasing melanin production.
Melanin is a protective pigment and ** a form of natural coloring. In other words, a tan or sunburn is the way of your skin to react and defend itself from exposure to the sun. Even if you do not burn, it is important to support your skin with protective clothing, sunscreen and shaded sanctuaries.
Knowledge is power

While the sun supports prosperity, excessive exposure can lead to skin aging and health concerns.
Understanding the effects of different types of solar and ultraviolet radiation can help you decide which sun care products are suitable for you. Regardless of your choice, make sure you include a High SPF wide range of sunscreen In your daily routine.
And above all, love your skin, take care of it and protect it, always.
Reports:
- GW Lambert, C Reid, DM Kaye, GL Jennings, MD Esler, Effect of Solar Light and Season on Serotonin Work on the Brain, The Lancet, Volume 360, Issue 9348, 2002, Pages 1840-1842
- Jean Krutmann, Anne Bouloc, Gabrielle Sore, Bruno A. Bernard, Thierry Passeron, The Exposome Aging Skin, Journal of Dermatological Science, Volume 85, Issue 3, 2017, pages 152-161
- Duteil L, Queille-Roussel C, Lacour JP, Montaudie H, Passeron T. Short-term exposure to blue light emitted by electronic devices does not aggravate the melasma. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2019.
- Khmaladze I, Leonardi M, Fabre S, Messaraa C, Mavon A. The interaction of the skin: a holistic “genome-micro-exposure” approach to understanding and regulating the health and aging of the skin. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2020; 13: 1021-1040. Published December 2020 24.
- Cho, S., Shin, M., Kim, Ys, Seo, J., Lee, YH, Park, Ch, & Chung, JW (2009). Effects of infrared radiation and heat on the aging of human skin in vivo. Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings, 14 (1), 15-19.


