Researchers reveal how gut microbes shape metabolic strategies to fuel bigger brains, offering a glimpse into primate evolutionary biology.
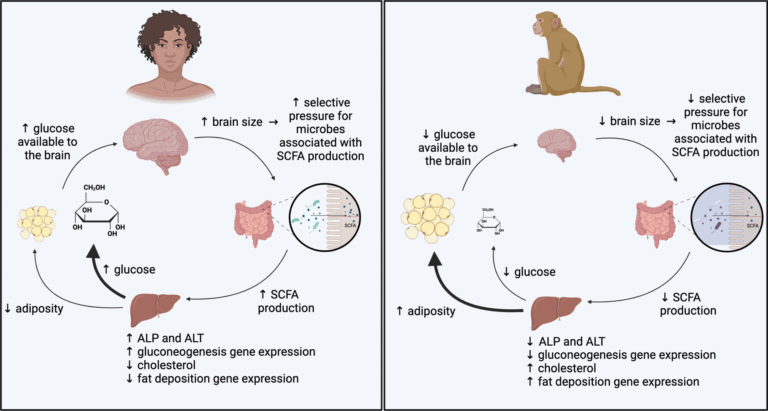
Hypothetical model for microbial effects on high- and low-EQ primate metabolism. Our findings indicate microbially mediated pathways through which the metabolism of high-EQ primates is directed toward energy production and the metabolism of low-EQ primates is directed toward energy storage.
In a recent study published in the journal Microbial Genomicsresearchers in the United States investigated the role of the gut microbiome in influencing host metabolism across species, focusing on primates with different brain sizes. They transferred gut microbial flora from humans, squirrel monkeys and macaques into germ-free mice and examined how microbial communities contribute to metabolic traits that may be linked to brain energy requirements and evolution.
Background
Large brains are energetically costly, especially in primates, where brain size is often associated with increased metabolic demands. Humans, with the largest brain-to-body size among primates, exhibit adaptations such as higher glucose metabolism to maintain these energy-intensive organs. However, the mechanisms driving these metabolic variations between species are poorly understood.
Existing research has reported the involvement of genetic and epigenetic factors in these metabolic variations, but their link to systemic metabolism remains unclear. The gut microbiome is a vital regulator of host metabolism and produces metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that affect energy storage, glucose production and fat metabolism. Moreover, while its role in metabolic diseases, including diabetes, is recognized, its contribution to metabolic differences between species, especially related to brain energy requirements, has been less explored.
About the Study
In the present study, the scientists hypothesized that differences in gut microbiota mediate metabolic strategies and balance energy needs for brain function against those for growth and maintenance in primates with different brain sizes. The researchers conducted an experiment using germ-free mice to investigate how the gut microbiome affects metabolism in hosts with different brain sizes.
The gut microbiota of three primate species, humans, squirrel monkeys, and macaques, were transplanted into germ-free mice to assess the effects of microbial differences on host metabolism. Humans and squirrel monkeys were chosen as brain-prioritizing species because of their larger brain sizes relative to body size, while macaques served as a comparison with a lower brain-to-body size ratio.
Fecal samples from healthy, antibiotic-free adult primates were collected, processed, and used to inoculate germ-free mice orally on a standard diet for 60 days. Weekly assessments included weight measurements, food consumption, and metabolic assessments, with stool and blood samples collected for microbiome and metabolite analyses. A glucose tolerance test was administered to measure glucose regulation, and mice underwent MRI to assess body fat distribution.
The researchers also used metagenomic and metabolomic analyzes to identify specific microbial pathways and metabolites that contribute to host metabolic traits. High-resolution imaging and ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequencing of liver tissues provided information on organ-specific metabolic responses. The microbial composition in the mouse gut was analyzed via 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) sequencing, while metagenomic techniques quantified SCFA production and microbial functional pathways.
Results
The results showed that the gut microbiome significantly influences host metabolism in ways consistent with the brain size of the primate species. Mice inoculated with gut microbiota from high-brain-to-body-sized species such as humans and squirrel monkeys showed increased energy expenditure, higher fasting glucose levels, and enhanced gluconeogenesis. In contrast, mice inoculated with microbiota from macaques showed greater fat accumulation and weight gain.
In addition, mice with microbiota from species with larger brain sizes consumed more food, but showed lower percentages of body fat and slower weight gain. Increased levels of SCFAs, such as acetate and propionate, were also observed in these mice, suggesting a microbial contribution to increased glucose production and reduced fat storage.
Metagenomic analysis revealed that microbial pathways related to energy production, such as fucose and pyruvate metabolism, were more abundant in high brain-to-body microbiota. Furthermore, expression of genes related to liver function in these mice revealed enrichment for pathways related to energy production, such as lipid metabolism and gluconeogenesis. These changes indicate metabolic programming aimed at prioritizing energy for brain function.
In contrast, mice inoculated with macaque microbiota exhibited microbial pathways that favor energy storage. Their microbiome produced lower concentrations of SCFAs and displayed functions aligned with fat deposition and reduced glucose production. These differences suggest a trade-off between brain versus adipose tissue energy allocation.
Interestingly, the human microbe-inoculated mice displayed unique metabolic profiles, with the highest fasting glucose and propionate levels, aligned with the extraordinary energy requirements of the human brain. Despite consuming more food, these mice had minimal weight gain, further highlighting the role of gut microbiota in metabolic regulation. Taken together, the results highlighted the ability of the gut microbiome to regulate host energy allocation strategies, reflecting the metabolic needs of the host species’ brain size and associated energy requirements.
conclusions
In conclusion, the study demonstrated the vital role of the gut microbiome in shaping host metabolic strategies and supporting the energy demands of larger brains in primates. The findings suggested that microbial communities influence glucose production, fat storage and energy allocation, providing insights into evolutionary adaptations to brain size.
The researchers noted that their findings provide the basis for investigating how microbiomes contribute to species-specific life history traits such as growth, reproduction and longevity. Future studies could investigate microbiome-host interactions during early developmental stages when brain energy demands peak.
Journal Reference:
- Mallott, EK, Kuthyar, S., Lee, W., Reiman, D., Jiang, H., Chitta, S., Alexandria, WE, Layden, BT, Sumagin, R., Manzanares, LD, Yang, G. -Y., Luisa, M., Gray, S., Williams, LE, Dai, Y., Curley, JP, Haney, CR, Liechty, ER, Kuzawa, CW, & Amato, KR (2024). The primate gut microbiota contributes to interspecific differences in host metabolism. Microbial Genomics10, 12. DOI:10.1099/mgen.0.001322,